For instance, AI systems like GPT-4 and Gemini can generate fluent text, understand complex language nuances, and process audio. These multimodal abilities have allowed AI to handle customer inquiries, generate detailed reports, and create personalised communications for clients. Additionally, AI’s pattern recognition and predictive analytics are already being used for risk assessment, property valuation, and fraud detection in the mortgage industry.
Case studies in financial services
A recent paper by Andrew W. Lo and Jillian Ross from MIT discussed the role of Generative AI in financial advice, indicating that AI could convincingly role-play as a financial advisor. They noted, “An LLM (Large Language Model) can roleplay a financial advisor convincingly and often accurately for a client.” This revelation is concerning for the mortgage sector, where client social interaction plays a crucial role. Could AI pretend to be as likeable as you actually are?
However, Lo and Ross also cautioned that AI lacks the sense of responsibility and ethics required by law from a human financial advisor. This caveat underscores the importance of human oversight in AI applications, ensuring that ethical standards and responsibilities are upheld.
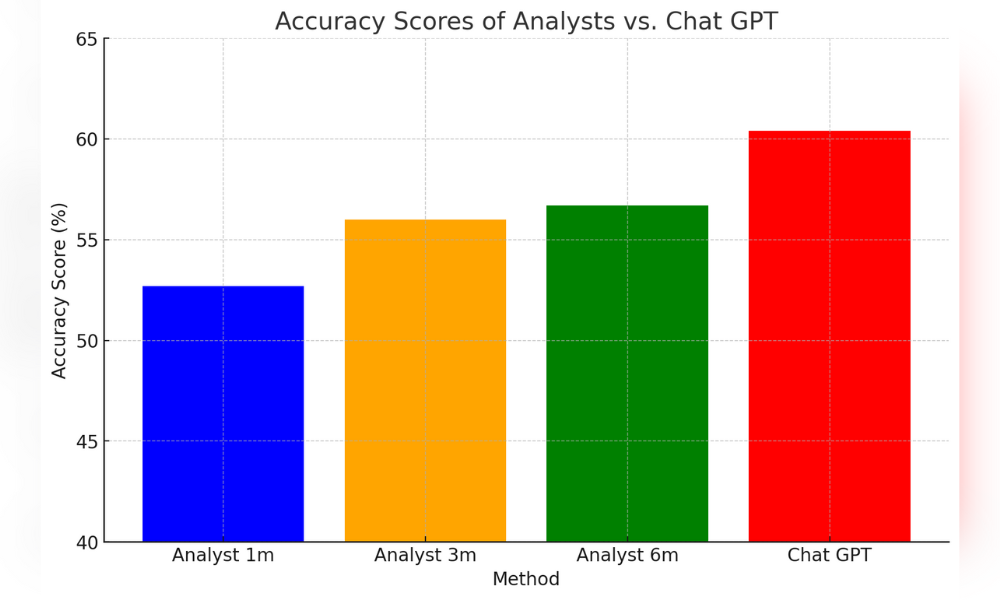
In another recent study from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business by Alex G. Kim, Maximilian Muhn, and Valeri V. Nikolaev, they revealed that GPT-4 could outperform human financial analysts in predicting earnings changes from financial statements. Using Chat GPT-4 Turbo, the researchers anonymized data and found that AI’s accuracy was significantly higher than that of human analysts. They concluded that trading strategies based on GPT-4’s predictions yielded higher Sharpe ratios and alphas compared to traditional models, indicating superior risk-adjusted returns.